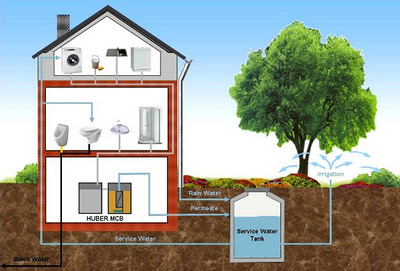
Enviroscape LA: Greywater Solutions for Landscape Irrigation
In response to years of drought in California, the State of California finalized emergency greywater standards. Greywater irrigation systems are now legal and can be installed without requiring a building permit (in many cases).
This new law will save millions of gallons of drinking water, water that is pumped hundreds of miles from the Sacramento and Colorado rivers at tremendous financial and ecological costs.
Greywater is water from the house, which is normally washed down the drain (such as laundry water) but is actually good for trees. In Los Angeles, California, there are a lot of reasons why we’re looking for new and innovative water sources, such as Greywater systems.